Virtual Environments are isolated environments. In contemporary software development, the need for isolated environments has become paramount to ensure the stability and integrity of systems.Tools such as npm, pip, flatpak, and others have emerged as indispensable solutions for creating isolated environments. Unlike traditional methods, these tools are designed to shield your system and other packages from potential conflicts and complications. By encapsulating applications and their dependencies, they not only enhance portability but also prevent pollution of the underlying system.
One notable example is the utilization of virtual environments in Python, where a specific Python version and its associated dependencies are encapsulated independently of the system-wide configurations. This isolation is crucial for maintaining project-specific requirements without affecting the overall system. This isolated environment operates as a self-contained unit, impervious to alterations in system-wide dependencies or Python versions. As a result, developers can confidently experiment with different versions of packages or Python itself within their project, secure in the knowledge that any changes made will not disrupt the stability of the broader system or conflict with other projects.
Methods to Create Virtual Environments in Python
-
venv
-
conda
-
mini-conda
-
pyenv
-
virtualenv
In this article, I focused on creating the virtual environment using venv. Other methods are similar.
Step 1: Create the Virtual Environment
$ python -m <module name> <module argument>
Now use the module venv to create the virtualenv called sample-env.
$ python -m venv sample-envIt will create a directory sample-env if it does not exist and then create a virtual environment called sample-env.
-
It creates a python binary in the directory
sample-env; if your system has multiple binaries, usepython2,python3, … in the first command instead ofpython. -
It also creates other files like
activate,activate.fish, etc.
Step 2: Activate the Virtual Environment
$ source sample-env/bin/activate-
It activates the given virtual environment.
-
activateis a bash script; useactivate.cshoractivate.fishdepending on your shell. -
The prompt changes.
(sample-env)is prepended before the original prompt. It tells you that you are in the virtual environmentsample-env.
Output:
(sample-env) $
Step 3: Do Anything in Virtual Environments
Now you can install/update any package or do anything without worrying about affecting your system outside the directory sample-env.
Install a Package Using pip
(sample-env) $ python -m pip install pywalOutput:
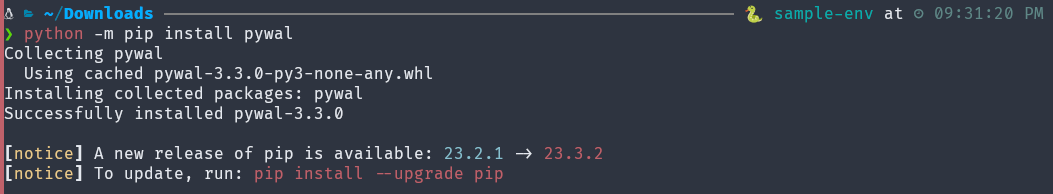
Install the Given Version of a Package Using pip
(sample-env) $ python -m pip install pywal==1.0.0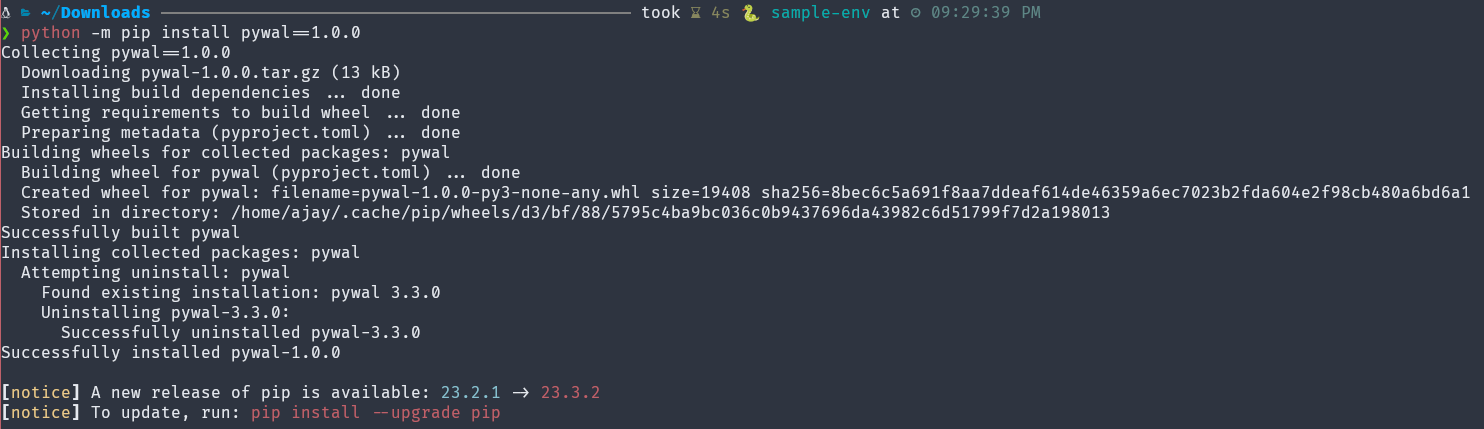
Upgrade a Package Using pip
(sample-env) $ python -m pip install --upgrade pywal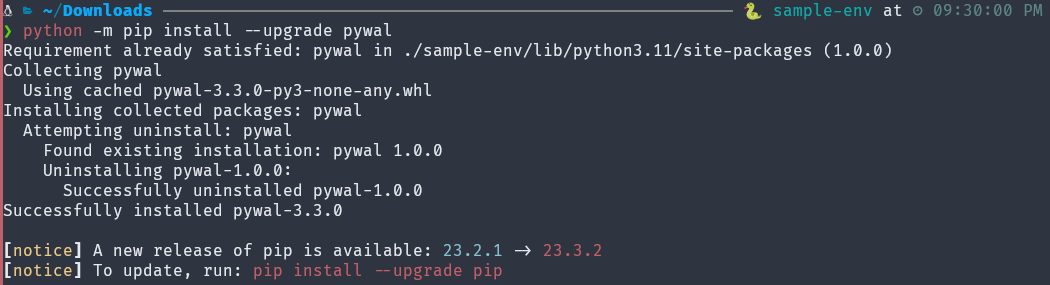
Uninstall Packages Using pip
(sample-env) $ python -m pip uninstall pywal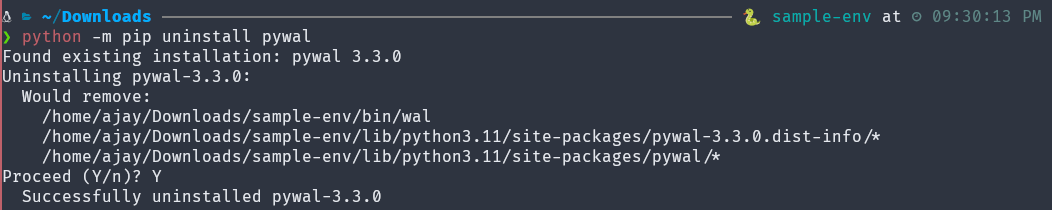
Display Information About a Package
(sample-env) $ python -m pip show beautifulsoup4show displays information about the given package which is installed.
Output:
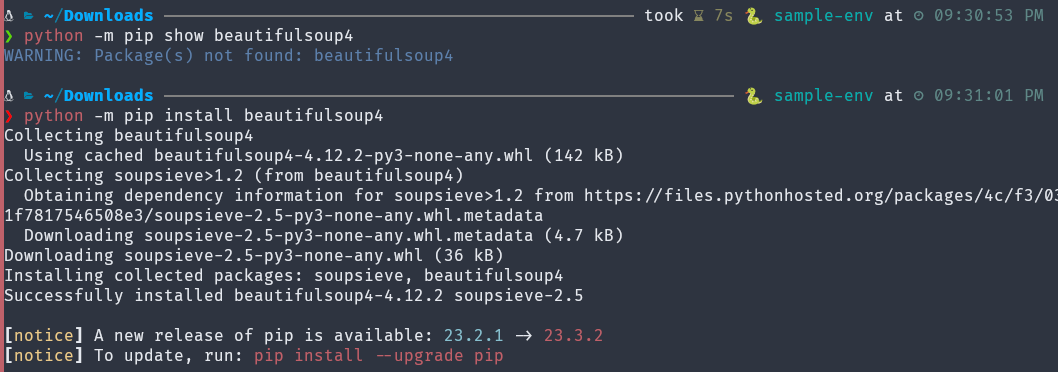
Display All Packages Installed in the Virtual Environment
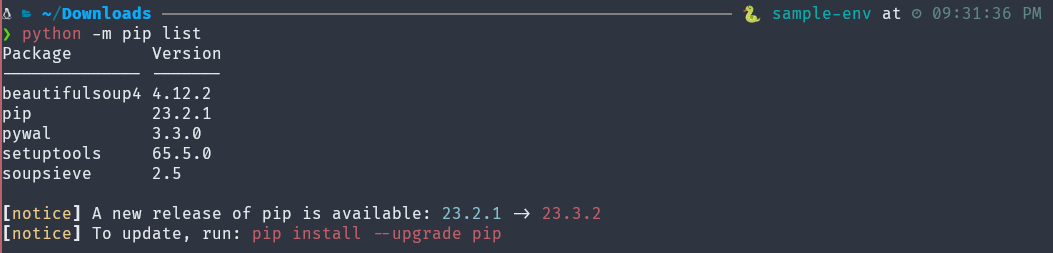
list displays all packages installed in the virtual environment:
(sample-env) $ python -m pip listOutput:
freeze is similar to list but used with > requirements.txt.
(sample-env) $ python -m pip freeze > requirements.txt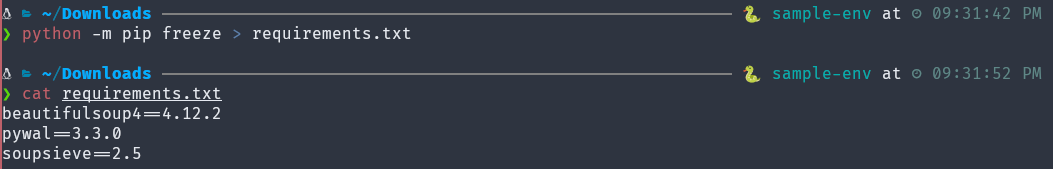
It is used for package shipment:
(sample-env) $ python -m pip install -r requirements.txtIt will install the packages mentioned in requirements.txt.
Output:
Collecting pywal==0.7.2 (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
...
Installing collected packages: pywal
Successfully installed pywal-0.7.2Step 4: Deactivate the Virtual Environment
(sample-env) $ deactivateConclusion
Virtual environments are essential tools in Python development, providing a controlled and isolated space for managing dependencies. Whether using venv or other methods, developers can confidently work on projects without worrying about conflicts or disruptions to the broader system. This flexibility enhances the development process, allowing for experimentation and version control while maintaining the overall stability of the system. Incorporating virtual environments into your workflow is a best practice that contributes to the reliability and reproducibility of Python projects.